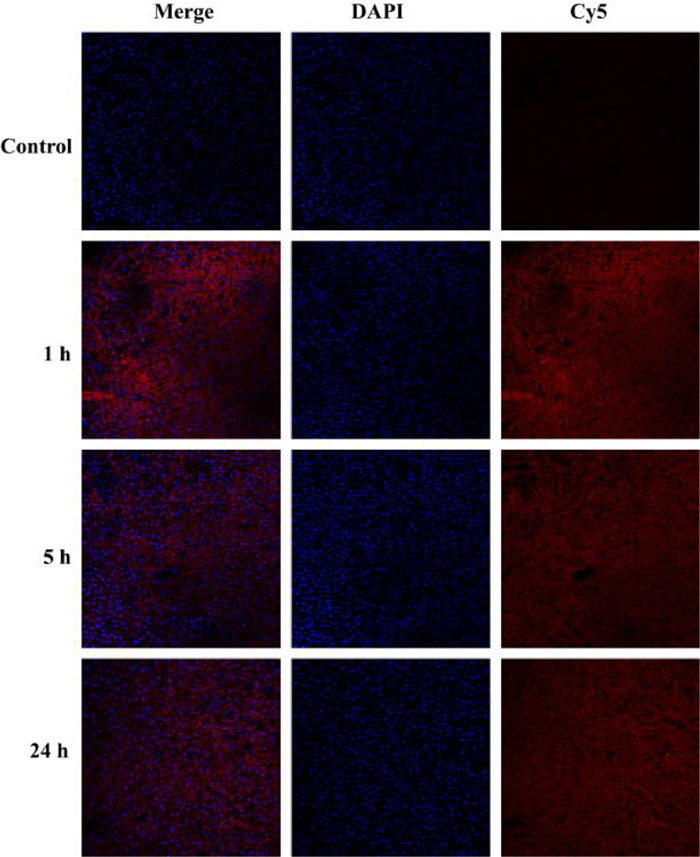
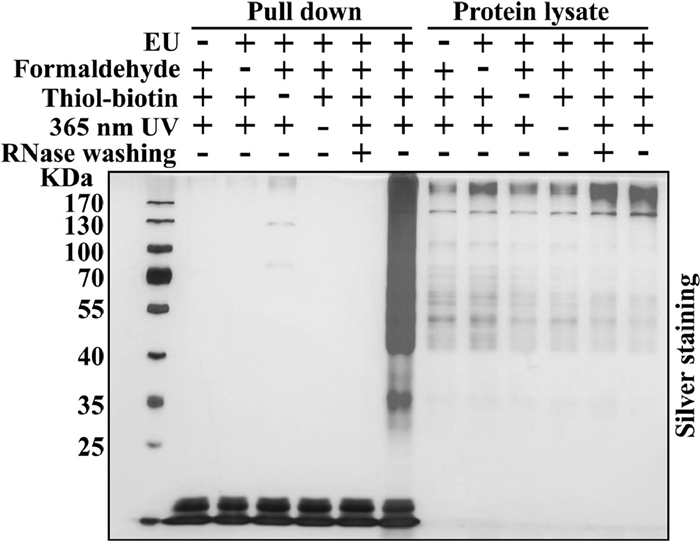
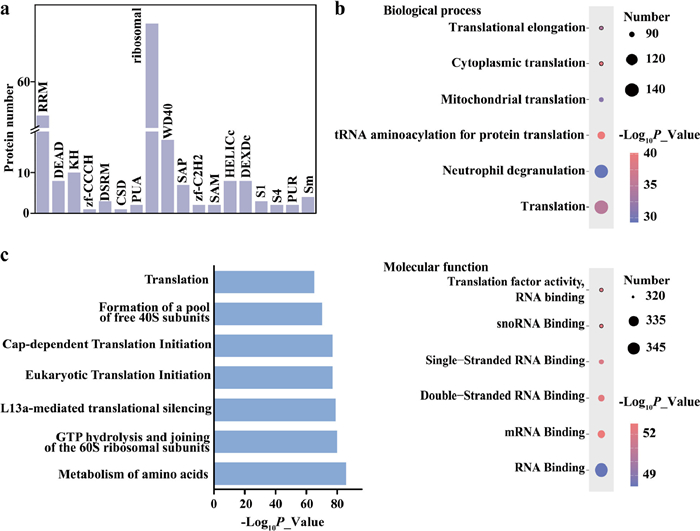
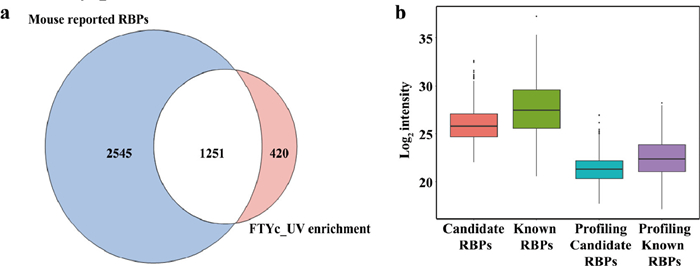
-
[1]
S.F. Mitchell, R. Parker, Mol. Cell 54 (2014) 547–558.
-
[2]
G. Singh, G. Pratt, G.W. Yeo, et al., Ann. Rev. Biochem. 84 (2015) 325–354.
-
[3]
Y.Y. Chen, Z. Gui, D. Hu, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 35 (2024) 108522.
-
[4]
M.W. Hentze, A. Castello, T. Schwarzl, et al., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19 (2018) 327–341.
-
[5]
S. Gerstberger, M. Hafner, T. Tuschl, Nat. Rev. Genet. 15 (2014) 829–845.
-
[6]
T. Feng, Y.L. Gao, D. Hu, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 35 (2024) 109259.
-
[7]
W.B. Tao, N.B. Xie, Q.Y. Cheng, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 34 (2023) 108243.
-
[8]
F. Gebauer, T. Schwarzl, J. Valcárcel, et al., Nat. Rev. Genet. 22 (2021) 185–198.
-
[9]
J.B. Bertoldo, S. Müller, S. Hüttelmaier, Drug Discov. Today 28 (2023) 103580.
-
[10]
Q. Zeng, S. Saghafinia, A. Chryplewicz, et al., Science 378 (2022) eabl7207.
-
[11]
K. Shi, X. Hong, D. Xu, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 36 (2025) 110079.
-
[12]
A. Castello, B. Fischer, K. Eichelbaum, et al., Cell 149 (2012) 1393–1406.
-
[13]
A.G. Baltz, M. Munschauer, B. Schwanhäusser, et al., Mol. Cell 46 (2012) 674–690.
-
[14]
B.M. Beckmann, R. Horos, B. Fischer, et al., Nat. Commun. 6 (2015) 10127.
-
[15]
A.M. Matia-González, E.E. Laing, A.P. Gerber, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22 (2015) 1027–1033.
-
[16]
X. Bao, X. Guo, M. Yin, et al., Nat. Methods 15 (2018) 213–220.
-
[17]
R. Huang, M. Han, L. Meng, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115 (2018) E3879–E3887.
-
[18]
R.M. Queiroz, T. Smith, E. Villanueva, et al., Nat. Biotechnol. 37 (2019) 169–178.
-
[19]
J. Trendel, T. Schwarzl, R. Horos, et al., Cell 176 (2019) 391–403. e319.
-
[20]
E.C. Urdaneta, C.H. Vieira-Vieira, T. Hick, et al., Nat. Commun. 10 (2019) 990.
-
[21]
Z. Zhang, T. Liu, H. Dong, et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (2021) e65 -e65.
-
[22]
H. Sun, B. Fu, X. Qian, et al., Nat. Commun. 15 (2024) 852.
-
[23]
W. Qin, S.A. Myers, D.K. Carey, et al., Nat. Commun. 12 (2021) 4980.
-
[24]
J. Yang, Y. Xu, Chin. Chem. Lett. 33 (2022) 2799–2806.
-
[25]
K. Yu, B. Chen, D. Aran, et al., Nat. Commun. 10 (2019) 3574.
-
[26]
A.F. Jarnuczak, H. Najgebauer, M. Barzine, et al., Sci. Data 8 (2021) 115.
-
[27]
R.P. Elinson, P. Pasceri, Development 106 (1989) 511–518.
-
[28]
V.O. Sysoev, B. Fischer, C.K. Frese, et al., Nat. Commun. 7 (2016) 12128.
-
[29]
A.T. LaPointe, N.N. Gebhart, M.E. Meller, et al., J. Virol. 92 (2018) e02171-17.
-
[30]
N.N. Gebhart, R.W. Hardy, K.J. Sokoloski, PLoS One 15 (2020) e0238254.
-
[31]
R.A. Flynn, J.A. Belk, Y. Qi, et al., Cell 184 (2021) 2394–2411 e2316.
-
[32]
T. Tayri-Wilk, M. Slavin, J. Zamel, et al., Nat. Commun. 11 (2020) 3128.
-
[33]
D.S. Johnson, A. Mortazavi, R.M. Myers, et al., Science 316 (2007) 1497–1502.
-
[34]
N.Z. Fantoni, A.H. El-Sagheer, T. Brown, Chem. Rev. 121 (2021) 7122–7154.
-
[35]
D.C. Kennedy, C.S. McKay, M.C. Legault, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 (2011) 17993–18001.
-
[36]
M.K. Singha, J. Zimak, S.R. Levine, et al., Biochemistry 61 (2022) 2638–2642.
-
[37]
M. Gupta, S.R. Levine, R.C. Spitale, Acc. Chem. Res. 55 (2022) 2647–2659.
-
[38]
R. Hoogenboom, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 20 (2010) 3415–3417.
-
[39]
J. Kaur, M. Saxena, N. Rishi, Bioconjugate Chem. 32 (2021) 1455–1471.
-
[40]
C.Y. Jao, A. Salic, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105 (2008) 15779–15784.
-
[41]
E.A. Hoffman, B.L. Frey, L.M. Smith, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 290 (2015) 26404–26411.
-
[42]
V. Jackson, Cell 15 (1978) 945–954.
-
[43]
M.F. Carey, C.L. Peterson, S.T. Smale, Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009 (2009) prot5279 pdb.
-
[44]
P.J. Boersema, R. Raijmakers, S. Lemeer, et al., Nat. Protoc. 4 (2009) 484–494.
-
[45]
A. Castello, M.W. Hentze, T. Preiss, Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 26 (2015) 746–757.
-
[46]
J. Boucas, C. Fritz, A. Schmitt, et al., PLoS One 10 (2015) e0125745.
-
[47]
S.C. Kwon, H. Yi, K. Eichelbaum, et al., Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20 (2013) 1122–1130.
-
[48]
Y. Liao, A. Castello, B. Fischer, et al., Cell Rep. 16 (2016) 1456–1469.
-
[49]
A. Liepelt, I.S. Naarmann-de Vries, N. Simons, et al., Mol. Cell. Proteomics 15 (2016) 2699–2714.
-
[50]
M. Ignarski, C. Rill, R.W. Kaiser, et al., J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 30 (2019) 564–576.
-
[51]
G. Du, X. Wang, M. Luo, et al., Development 147 (2020) dev184655.
-
[52]
C. He, S. Sidoli, R. Warneford-Thomson, et al., Mol. Cell 64 (2016) 416–430.
-
[53]
A.L. Mallam, W. Sae-Lee, J.M. Schaub, et al., Cell Rep. 29 (2019) 1351–1368. e1355.
-
[54]
Y. Na, H. Kim, Y. Choi, et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (2021) e28 -e28.
-
[55]
J.I. Perez-Perri, D. Ferring-Appel, I. Huppertz, et al., Nat. Commun. 14 (2023) 2074.
-
[56]
K.B. Cook, H. Kazan, K. Zuberi, et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 39 (2010) D301–D308.
-
[57]
M. Caudron-Herger, R.E. Jansen, E. Wassmer, et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (2021) D425–D436.

 Login In
Login In






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: