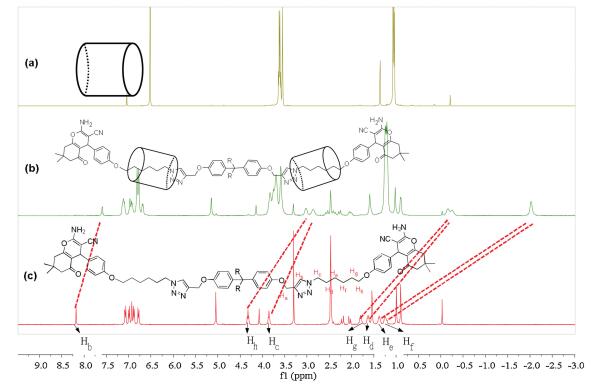
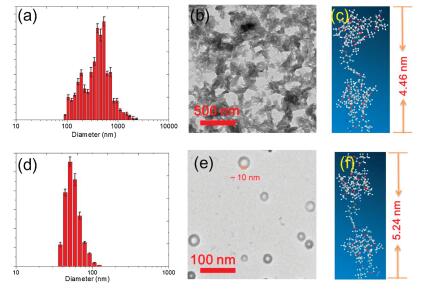
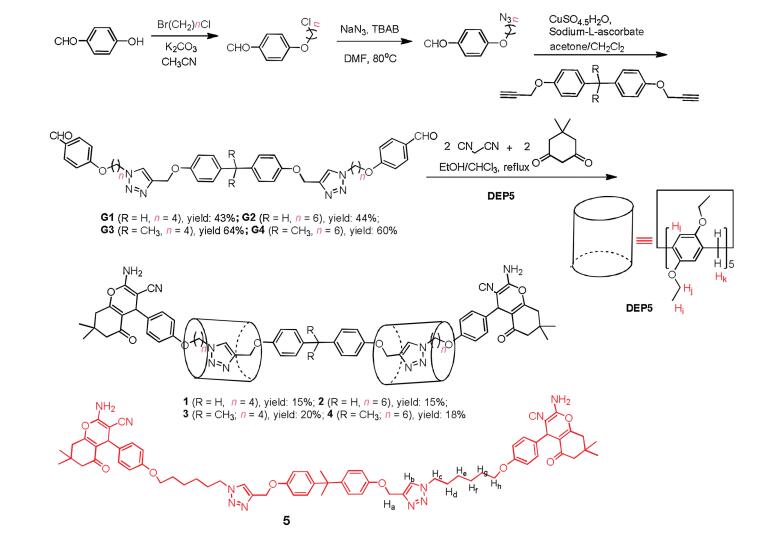
-
[1]
(a) K.D. Hanni, D.A. Leigh, Chem. Soc. Rev. 39 (2010) 1240-1251;
(b) M.D. Lankshear, P.D. Beer, Acc. Chem. Res. 40 (2007) 657-668;
(c) T. Ikeda, M. Higuchi, D.G. Kurth, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (2009) 9158-9159;
(d) M. He, L. Chen, B. Jiang, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 30 (2019) 131-134.
-
[2]
(a) T. Ogoshi, D. Yamafuji, T. Aoki, T.A. Yamagishi, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 48 (2012) 6842-6844;
(b) Y. Yao, X.J. Wei, Y. Cai, et al., J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 533 (2019) 42-46.
-
[3]
E.M.G. Jamieson, F. Modicom, S.M. Goldup, Chem. Soc. Rev. 47(2018) 5266-5311.
doi: 10.1039/C8CS00097B
-
[4]
(a) Y. Liu, Q. Zhang, W.H. Jin, et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 54 (2018) 10642-10645;
(b) T.G. Zhan, H.H. Yin, S.T. Zheng, et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 54 (2018) 9356-9359;
(c) G. Gholami, K. Zhu, G. Baggi, et al., Chem. Sci. 8 (2017) 7718-7723;
(d) W. Wu, S. Song, X. Cui, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 29 (2018) 95-98;
(e) R. Zhang, C. Wang, R. Long, et al., Front. Chem. 7 (2019) 508.
-
[5]
T. Ogoshi, S. Kanai, S. Fujinami, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 (2008) 5022-5023.
doi: 10.1021/ja711260m
-
[6]
(a) S. Sun, D. Lu, Q. Huang, et al., Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 533 (2019) 42-46;
(b) S. Sun, M. Geng, L. Huang, et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 54 (2018) 13006-13009;
(c) K. Jie, Y. Zhou, E. Li, et al., Acc. Chem. Res. 51 (2018) 2064-2072;
(d) Y. Zhang, W. Zhu, X. Huang, et al., ACS Sust. Chem.Eng. 6 (2018)16597-16606;
(e) E. Li, K. Jie, Y. Zhou, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140 (2018) 15070-15079;
(f) J.R. Wu, A. Mu, B. Li, et al., Angew. Chem. Ing. Ed. 57 (2018) 9853-9858;
(g) M. Zuo, W. Qian, Z. Xu, et al., Small 14 (2018) 1801942;
(h) L.L. Zhao, Y. Han, C.G. Yan, Chin. Chem. Lett. 31 (2020) 81-83;
(i) C.B. Yin, Y. Han, G.F. Huo, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 28 (2017) 431-436;
(j)J.Chen, Y.Wang, C.Wang, etal., Chem.Commun.(Camb.)55 (2019)6817-6826.
-
[7]
(a) T. Xiao, L. Zhou, L. Xu, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 30 (2019) 271-276;
(b) T. Xiao, W. Zhong, L. Xu, X.Q. Sun, X.Y. Hu, L. Wang, Org. Biomol. Chem. 17 (2019) 1336-1350;
(c) Y. Wang, T. Liu, J. Jiang, et al., Dalton Trans. 48 (2019) 6333-6336.
-
[8]
(a) Q. Wang, L. Tian, J. Xu, et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 54 (2018) 10328-10331;
(b) K. Yang, K. Yang, S. Chao, et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 54 (2018) 9817-9820;
(c) H. Shi, X. Cheng, Q. Lin, et al., Chin. J. Org. Chem. 38 (2018) 1718-1724;
(d) Y. Sun, F. Zhang, J. Quan, et al., Nat. Comm. 9 (2018) 2617;
(e) J.Y. Chen, W.W. Hao, M. Zhang, et al., Faraday Discuss. 209 (2018) 149-159;
(f) J. Wu, J. Tian, L. Rui, W. Zhang, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 54 (2018) 7629-7632.
-
[9]
(a) X.S. Du, C.Y. Wang, Q. Jia, et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 53 (2017) 5326-5329;
(b) S. Dong, J. Yuan, F. Huang, Chem. Sci. 5 (2014) 247-252;
(c) X. Zeng, H. Deng, X. Jia, et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 54 (2018) 11634-11637;
(d) Y. Han, C.Y. Nie, S. Jiang, J. Sun, C.G. Yan, Chin. Chem. Lett. 31 (2020) 725-728.
-
[10]
C.L. Sun, K.X. Teng, L.Y. Niu, Y.Z. Chen, Q.Z. Yang, Acta Chim. Sinica 76 (2018) 779-784.
doi: 10.6023/A18070258
-
[11]
D. Xia, P. Wei, B. Shi, F. Huang, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 52 (2016) 513-516
doi: 10.1039/C5CC08038J

 Login In
Login In






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: