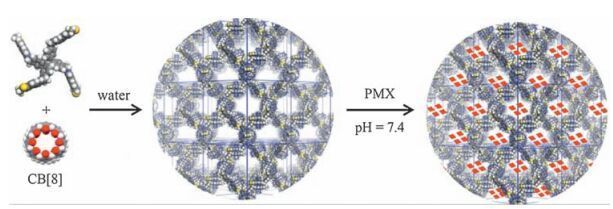
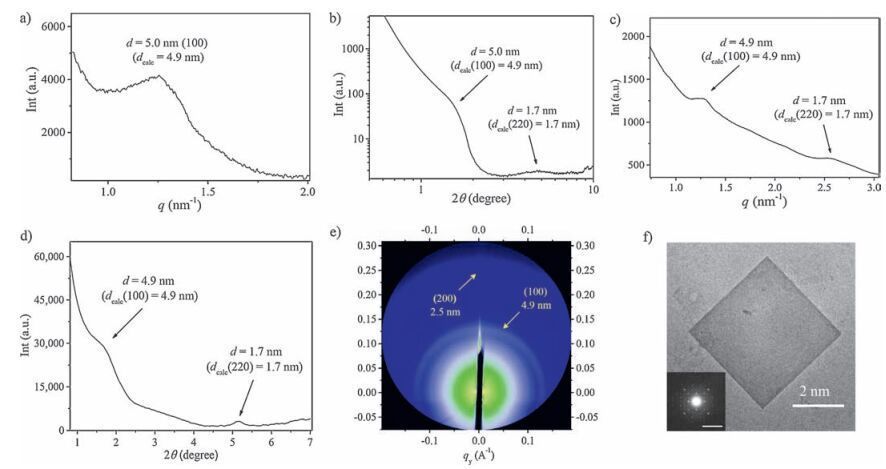
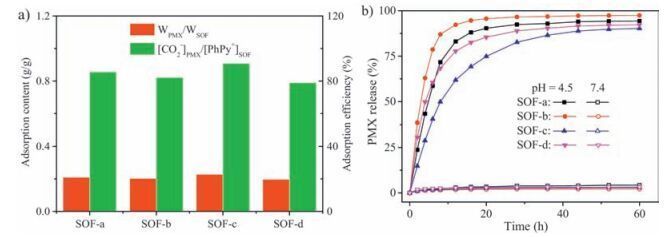
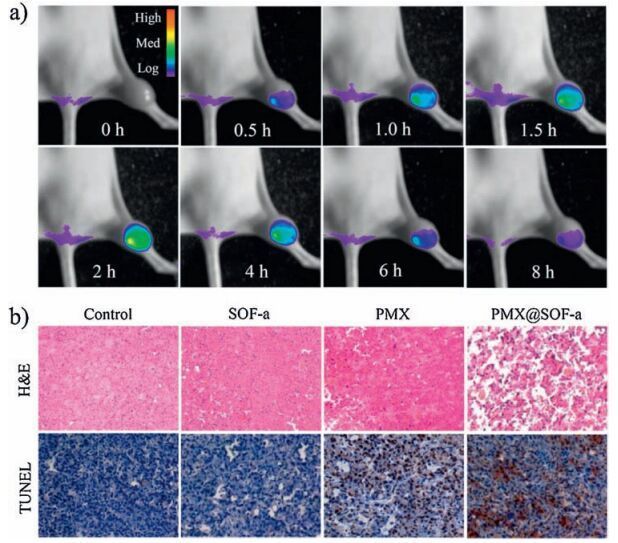
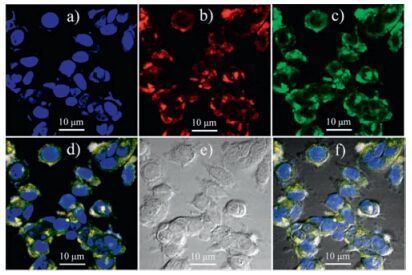
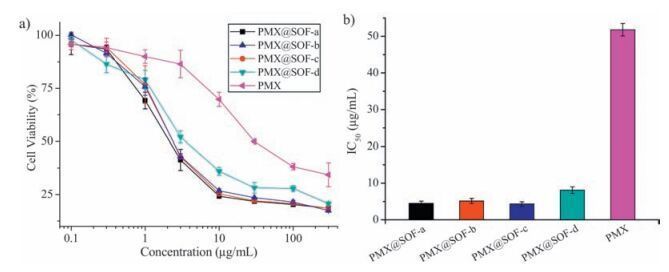
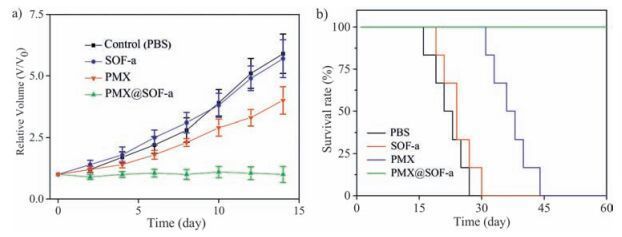
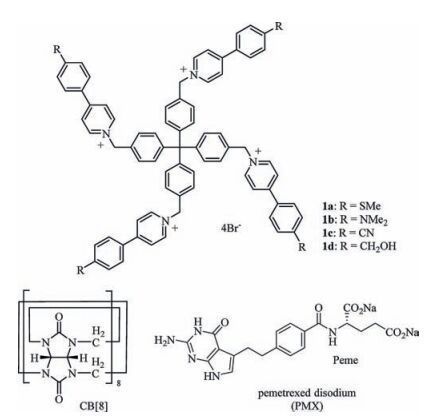
-
[1]
A. K. Mitra, C. H. Lee, K. Cheng(Eds. ), Advanced Drug Delivery, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, 2014 513 pp.
-
[2]
(a)G. Ma, et al. , Acyclic cucurbit[n] uril molecular containers enhance the solubility and bioactivity of poorly soluble pharmaceuticals, Nature Chem. (2012);
(b)D. S. Guo, K. Wang, Y. X. Wang, Y. Liu, Cholinesterase-responsive supramolecular vesicle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(2012)10244-10250;
(c)R. Tong, L. Tang, L. Ma, C. Tu, R. Baumgartner, J. Cheng, Smart chemistry in polymeric nanomedicine, Chem. Soc. Rev. 43(2014)6982-7012;
(d)Y. Cao, X. Y. Hu, Y. Li, et al. , Multistimuli-responsive supramolecular vesicles based on water-soluble pillar[6] arene and SAINT complexation for controllable drug release, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(2014)10762-10769;
(e)Y. X. Wang, D. S. Guo, Y. C. Duan, Y. J. Wang, Y. Liu, Amphiphilic p-sulfonatocalix[4] arene as drug chaperone for escorting anticancer, Drugs Sci. Rep. 5(2015)9019;
(f)P. T. Zhang, L. Shi Huang, et al. , Self-assembled nanoparticles of amphiphilic twin drug from floxuridine and bendamustine for cancer therapy, Mol. Pharm. 12(2015)2328-2336;
(g)C. Yao, P. Wang, X. Li, et al. , Near-infrared-triggered azobenzene-liposome/upconversion nanoparticle hybrid vesicles for remotely controlled drug delivery to overcome cancer multidrug resistance, Adv. Mater. 28(2016)9341-9348;
(h)Y. Zhou, H. Li, Y. W. Yang, Controlled drug delivery systems based on calixarenes, Chin. Chem. Lett. 26(2015)825-828;
(i)Y. Z. Chen, Y. K. Huang, Y. Chen, et al. , Novel nanoparticles composed of chitosan and b-cyclodextrin derivatives as potential insoluble drug carrier, Chin. Chem. Lett. 26(2015)909-913;
(j)C. Wang, H. Zhang, D. Zeng, L. San, X. Mi, DNA nanotechnology mediated gold nanoparticle conjugates and their applications in biomedicine, Chin. J. Chem. 34(2016)299-307;
(k)R. Jia, T. Wang, Q. Jiang, et al. , Self-assembled DNA nanostructures for drug delivery, Chin. J. Chem. 34(2016)265-272;
(l)J. Sun, J. Wang, Z. Yang, Supramolecular assembly models of siRNA delivery systems, Chin. J. Chem. 33(2015)79-89;
(m)Y. Wang, Y. Liu, Supramolecular assemblies based on p-sulfonatocalixarenes and their functions, Acta Chim. Sinica 73(2015)984-991;
(n)S. Peng, J. Gao, Y. Liu, D. S. Guo, Facile fabrication of cross-linked vesicle via surface clicking of calixarene-based supra-amphiphiles, Chem. Commun. 51 (2015)16557-16560;
(o)X. Wu, L. Gao, X. Y. Hu, et al. , Supramolecular drug delivery systems based on water-soluble pillar[n] arenes, Chem. Rec. 16(2016)1216-1227.
-
[3]
(a)R. Tanbour, A. M. Martins, W. G. Pitt, G. A. Husseini, Drug delivery systems based on polymeric micelles and ultrasound: a review, Curr. Pharm. Des. 22 (2016)2796-2807;
(b)T. M. Allen, P. R. Cullis, Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 65(2013)36-48;
(c)K. Wang, D. S. Guo, X. Wang, Y. Liu, Multistimuli responsive supramolecular vesicles based on the recognition of p-sulfonatocalixarene and its controllable release of doxorubicin, ACS Nano 5(2011)2880-2894;
(d)L. Zhao, J. Ding, C. Xiao, et al. , Poly(L-glutamic acid)microsphere: preparation and application in oral drug controlled release, Sinica Acta Chim. 73(2015)60-65.
-
[4]
(a)H. Wang, Q. Huang, H. Chang, J. Xiao, Y. Cheng, Stimuli-responsive dendrimers in drug delivery, Biomater. Sci. 4(2016)375-390;
(b)Y. Zhou, W. Huang, J. Liu, X. Zhu, D. Yan, Self-assembly of hyperbranched polymers and its biomedical applications, Adv. Mater. 22(2010)4567-4590;
(c)S. Zhang, J. Yang, M. Liu, et al. , Synthesis of peptide dendrimers and their application in the drug delivery system, Huaxue Xuebao 74(2016)401-409.
-
[5]
(a)H. Q. Wu, C. C. Wang, Biodegradable smart nanogels: a new platform for targeting drug delivery and biomedical diagnostics, Langmuir 32(2016)6211-6225;
(b)S. Liu, Y. Zhou, F. Chen, et al. , Rheological properties, drug release behavior and cytocompatibility of novel hydrogels prepared from carboxymethyl chitosan, Sinica Acta Chim. 73(2015)47-52.
-
[6]
(a)M. Prato, K. Kostarelos, A. Bianco, Functionalized carbon nanotubes in drug design and discovery, Acc. Chem. Res. 41(2008)60-68;
(b)F. Du, J. Xu, F. Zeng, S. Wu, Preparation of a multifunctional nano-carrier system based on carbon dots with pH-triggered drug release, Sinica Acta Chim. 74(2016)241-250.
-
[7]
(a)I. Brigger, C. Dubernet, P. Couvreur, Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 54(2002)631-651;
(b)P. Yang, S. Gai, J. Lin, Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery, Chem. Soc. Rev. 41(2012)3679-3698;
(c)T. Sun, Y. S. Zhang, B. Pang, et al. , Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53(2014)12320-12364;
(d)Z. Tang, C. He, H. Tian, et al. , Polymeric nanostructured materials for biomedical applications, Progr. Polym. Sci. 60(2016)86-128;
(e)Y. J. Chang, X. Z. Liu, Q. Zhao, et al. , P(VPBA-DMAEA)as a pH-sensitive nanovalve for mesoporous silica nanoparticles based controlled release, Chin. Chem. Lett. 26(2015)1203-1208;
(f)H. Liang, H. Tian, M. Deng, X. Chen, Gold nanoparticles for cancer theranostics, Chin. J. Chem. 33(2015)1001-1010;
(g)P. Yang, L. Wang, H. Wang, Smart supramolecular nanosystems for bioimaging and drug delivery, Chin. J. Chem. 33(2015)59-70;
(h)X. Wang, L. Tan, Y. Yang, Controlled drug release systems based on mesoporous silica capped by gold nanoparticles, Sinica Acta Chim. 74(2016) 303-311.
-
[8]
(a)J. Nicolas, Drug-initiated synthesis of polymer prodrugs: combining simplicity and efficacy in drug delivery, Chem. Mater. 28(2016)1591-1606;
(b)Z. Du, Y. Zhang, J. Ye, H. Xu, M. Lang, Synthesis and properties of the poly (e-caprolactone)-paclitaxel prodrug, Acta Chim. Sinica 73(2015)349-356.
-
[9]
(a)E. Fleige, M. A. Quadir, R. Haag, Stimuli-responsive polymeric nanocarriers for the controlled transport of active compounds: concepts and applications, Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 64(2012)866-884;
(b)S. Mura, J. Nicolas, P. Couvreur, Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery, Nat. Mater. 12(2013)991-1003;
(c)R. Cheng, F. Meng, C. Deng, H. A. Klok, Z. Zhong, Dual and multi-stimuli responsive polymeric nanoparticles for programmed site-specific drug delivery, Biomaterials 34(2013)3647-3657;
(d)Z. Ge, S. Liu, Functional block copolymer assemblies responsive to tumor and intracellular microenvironments for site-specific drug delivery and enhanced imaging performance, Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(2013)7289-7325;
(e)Q. Yin, J. Shen, Z. Zhang, H. Yu, Y. Li, Reversal of multidrug resistance by stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems for therapy of tumor, Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 65(2013)1699-1715.
-
[10]
(a)D. Schmaljohann, Thermo-and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58(2006)1655-1670;
(b)W. W. Gao, J. M. Chan, O. C. Farokhzad, pH-Responsivenanoparticles fordrug delivery, Mol. Pharm. 7(2010)1913-1920;
(c)J. Liu, Y. Huang, A. Kumar, et al. , pH-Sensitive nano-systems for drug delivery in cancer therapy, Biotech Adv. 32(2014)693-710;
(d)Y. J. Zhu, F. Chen, pH-Responsive drug-delivery systems, Chem. Asian J. 10 (2015)284-305.
-
[11]
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs.
-
[12]
(a)D. Pissuwan, T. Niidome, M. B. Cortie, The forthcoming applications of gold nanoparticles in drug and gene delivery systems, J. Controll. Release 149(2011) 65-71;
(b)X. Guo, L. Huang, Recent advancesinnonviralvectorsfor genedelivery, Acc. Chem. Res. 45(2012)971-979;
(c)X. Ma, Y. Zhao, Biomedical applications of supramolecular systems based on host-guest interactions, Chem. Rev. 115(2015)7794-7839.
-
[13]
(a)J. Tian, L. Chen, D. W. Zhang, Y. Liu, Z. T. Li, Supramolecular organic frameworks: engineering periodicity in water through host-guest chemistry, Chem. Commun. 52(2016)6351-6362;
(b)K. D. Zhang, J. Tian, D. Hanifi, et al. , Toward a single-layer two-dimensional honeycomb supramolecular organic framework in water, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (2013)17913-17918;
(c)J. Tian, T. Y. Zhou, S. C. Zhang, et al. , Three-dimensional periodic supramolecular organic framework ion sponge in water and microcrystals, Nat. Commun. 5(2014)5574;
(d)J. Tian, Z. Y. Xu, D. W. Zhang, et al. , Supramolecular metal-organic frameworks that display high homogeneous and heterogeneous photocatalytic activity for H2 production, Nat. Commun. 7(2016)11580;
(e)L. Chen, Y. C. Zhang, W. K. Wang, et al. , Conjugated radical cation dimerization-driven generation of supramolecular architectures, Chin. Chem. Lett. 26(2015)811-816;
(f)H. Wang, D. W. Wang, Z. T. Li, Supramolecular organic frameworks(SOFs): water-phase periodic porous self-assembled architectures, Sinica Acta Chim. 73(2015)471-479;
(g)T. Wan, T. Li, From supramolecular polymers to supramolecular organic frameworks: Engineering the periodicity of solution-phase self-assembled architectures, Photochem. Imag. Sci. 33(2015)3-14;
(h)L. Zhang, Y. Jia, H. Wang, et al. , pH-Responsive single-layer honeycomb supramolecular organic frameworks that exhibit antimicrobial activity, Polym. Chem. 7(2016)1861-1865;
(i)L. Zhang, T. Y. Zhou, J. Tian, et al. , A two-dimensional single-layer supramolecular organic framework that is driven by viologen radical cation dimerization and further promoted by cucurbit[8] uril, Polym. Chem. 5(2014) 4715-4721.
-
[14]
Pfeffermann M., Dong R., Graf R.. Free-standing monolayer two-dimensional supramolecular organic framework with good internal order[J]. J. Am.Chem.Soc.,
2015,137:14525-14532.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b09638
-
[15]
(a)Y. Zhang, T. G. Zhan, T. Y. Zhou, et al. , Fluorescence enhancement through the formation of a single-layer two-dimensional supramolecular organic framework and its application in highly selective recognition of picric acid, Chem. Commun. 52(2016)7588-7591;
(b)S. Q. Xu, X. Zhang, C. B. Nie, et al. , The construction of a two-dimensional supramolecular organic framework with parallelogram pores and stepwise fluorescence enhancement, Chem. Commun. 51(2015)16417-16420.
-
[16]
(a)Y. H. Ko, E. Kim, I. Hwang, K. Kim, Supramolecular assemblies built with host-stabilized charge-transfer interactions, Chem. Commun. (2007)1305-1315;
(b)Z. J. Zhang, Y. M. Zhang, Y. Liu, Controlled molecular self-assembly behaviors between cucurbituril and bispyridinium derivatives, J. Org. Chem. 76(2011) 4682-4685;
(c)Y. Liu, H. Yang, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, Controlled molecular self-assembly behaviors between cucurbituril and bispyridinium derivatives, Chem. Asian J. 8(2013)1626-1632;
(d)J. Liu, C. S. Y. Tan, Y. Lan, O. A. Scherman, Aqueous polymer self-assembly based on cucurbit[n] uril-mediated host-guest interactions, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 217(2016)319-332;
(e)J. Tian, L. Zhang, H. Wang, D. W. Zhang, Z. T. Li, Supramolecular polymers and networks driven by cucurbit[8] uril-guest pair encapsulation in water, Supramol. Chem. 28(2016)769-783.
-
[17]
Liu S., Ruspic C., Mukhopadhyay P., Chakrabarti S., Zavalij P.Y., Isaacs L. The cucurbit[n] uril family:prime components for self-sorting systems[J]. J.Am. Chem.Soc.,
2005,127:15959-15967.
doi: 10.1021/ja055013x
-
[18]
(a)J. Fang, H. Nakamura, H. Maeda, The EPR effect: unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63(2011)136-151;
(b)Y. Barenholz, Doxil1, The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned, J. Control. Release 160(2012)117-134.
-
[19]
Accelrys Materials Studio Release Notes, Release 5. 0, Accelrys Software Inc, San Diego, 2008.
-
[20]
(a)M. H. Cohen, R. Justice, R. Pazdur, Approval summary: pemetrexed in the initial treatment of advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, Oncologist 14(2009)930-935;
(b)M. Hazarika, R. M. White, J. R. Johnson, R. Pazdur, FDA drug approval summaries: pemetrexed(Alimta®), Oncologist 9(2004)482-488.
-
[21]
Vandana M., Sahoo S.K. Reduced folate carrier independent internalization of PEGylated pemetrexed:a potential nanomedicinal approach for breast cancer therapy[J]. Mol.Pharm.,
2012,9:2828-2843.
doi: 10.1021/mp300131t
-
[22]
Pluen Y.. Role of tumor-host interactions in interstitial diffusion of macromolecules:cranial vs.subcutaneous tumors[J]. Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A.,
2001,98:4628-4633.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.081626898
-
[23]
Eldin E.N., Elnahas H.M., Mahdy M.A.E., Ishida T. Liposomal pemetrexed: formulation, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity studies for effective management of malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Biol.Pharm.Bull.,
2015,38:461-469.
doi: 10.1248/bpb.b14-00769
-
[24]
Han J., Burgess K. Fluorescent indicators for intracellular pH[J]. Chem.Rev.,
2010,110:2709-2728.
doi: 10.1021/cr900249z
-
[25]
Tian Y., Jiang X., Chen X., Shao Z., Yang W. Doxorubicin-loaded magnetic silk fibroin nanoparticles for targeted therapy of multidrug-resistant cancer[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2014,26:7393-7398.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.43
-
[26]
Tang S., Yin Q., Zhang Z.. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and RNA using pH-sensitive poly(b-amino ester)nanoparticles for reversal of multidrug resistance of breast cancer[J]. Biomaterials,
2014,35:6047-6059.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.025

 Login In
Login In






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: