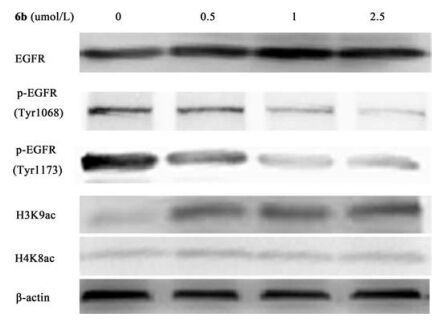
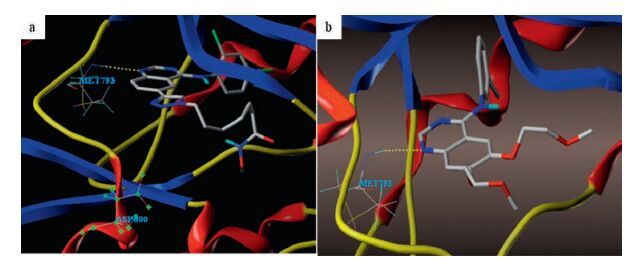
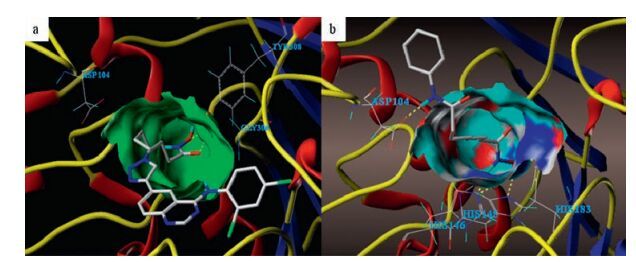
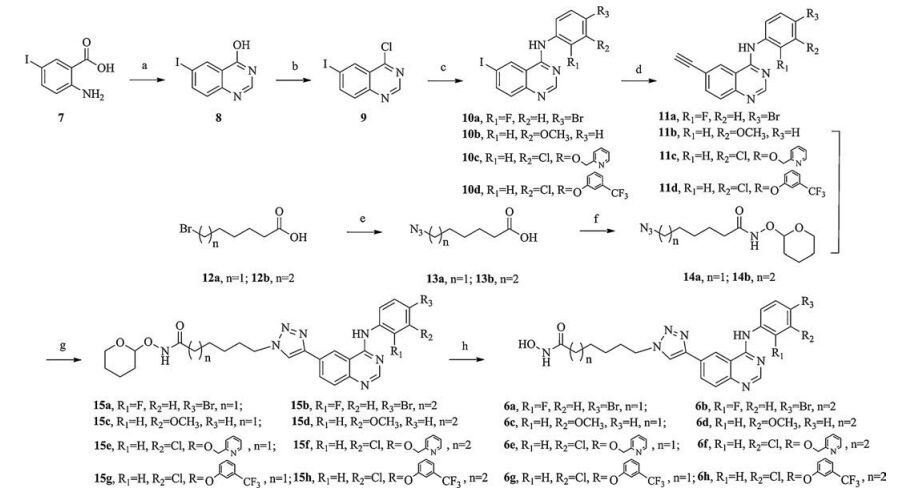
-
[1]
Taby R., Issa J.P.J.. Cancer epigenetics[J]. CA Cancer J. Clin.,
2010,60:376-392.
doi: 10.3322/caac.20085
-
[2]
Mann B.S., Johnson J.R., Cohen M.H., Justice R., Pazdur R.. FDA approval summary:vorinostat for treatment of advanced primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma[J]. Oncologist,
2007,12:1247-1252.
doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-10-1247
-
[3]
Ellis L., Pan Y., Smyth G.K.. Histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat induces clinical responses with associated alterations in gene expression profiles in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma[J]. Clin. Cancer Res.,
2008,14:4500-4510.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4262
-
[4]
Grant C., Rahman F., Piekarz R.. Romidepsin:a new therapy for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and a potential therapy for solid tumors[J]. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther.,
2010,10:997-1008.
doi: 10.1586/era.10.88
-
[5]
Yu C., Friday B.B., Lai J.P.. Abrogation of MAPK and Akt signaling by AEE788 synergistically potentiates histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species generation[J]. Clin. Cancer Res.,
2007,13:1140-1148.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1751
-
[6]
Jane E.P., Premkumar D.R., Addo-Yobo S.O., Pollack I.F.. Abrogation of mitogenactivated protein kinase and Akt signaling by vandetanib synergistically potentiates histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in human Glioma cells[J]. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.,
2009,331:327-337.
doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.155705
-
[7]
Mahboobi S., Dove S., Sellmer A.. Design of chimeric histone deacetylaseand tyrosine kinase-inhibitors:a series of imatinib hybrides as potent inhibitors of wild-type and mutant BCR-ABL, PDGF-Rb, and histone deacetylases[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2009,52:2265-2279.
doi: 10.1021/jm800988r
-
[8]
Cai X., Zhai H.X., Wang J.. Discovery of 7-(4-(3-Ethynylphenylamino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yloxy)-N-hydroxyheptanamide (CUDC-101) as a potent multi-acting HDAC, EGFR, and HER2 inhibitor for the treatment of cancer[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2010,53:2000-2009.
doi: 10.1021/jm901453q
-
[9]
Mahboobi S., Sellmer A., Winkler M.. Novel chimeric histone deacetylase inhibitors:a series of lapatinib hybrides as potent inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2(HER2), and histone deacetylase activity,[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2010,53:8546-8555.
doi: 10.1021/jm100665z
-
[10]
Li Y., Tan C., Gao C.. Discovery of benzimidazole derivatives as novel multi-target EGFR, VEGFR-2 and PDGFR kinase inhibitors[J]. Bioorg. Med. Chem.,
2011,19:4529-4535.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.06.022
-
[11]
Luan X., Gao C., Zhang N.. Exploration of acridine scaffold as a potentially interesting scaffold for discovering novel multi-target VEGFR-2 and Src kinase inhibitors[J]. Bioorg. Med. Chem.,
2011,19:3312-3319.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.04.053
-
[12]
Zhang C., Tan C., Zu X.. Exploration of (S)-3-aminopyrrolidine as a potentially interesting scaffold for discovery of novel Abl and PI3 K dual inhibitors[J]. Eur. J. Med. Chem.,
2011,46:1404-1414.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.01.020
-
[13]
Jin F., Gao D., Wu Q.. Exploration of N-(2-aminoethyl)piperidine-4-carboxamide as a potential scaffold for development of VEGFR-2, ERK-2 and Abl-1 multikinase inhibitor[J]. Bioorg. Med. Chem.,
2013,21:5694-5706.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.07.026
-
[14]
Jin F., Gao D., Zhang C.. Exploration of 1-(3-chloro-4-(4-oxo-4Hchromen-2-yl)phenyl)-3-phenylurea derivatives as selective dual inhibitors of Raf1 and JNK1 kinases for anti-tumor treatment[J]. Bioorg. Med. Chem.,
2013,21:824-831.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.04.006
-
[15]
Lang X.L., Sun Q.S., Chen Y.Z.. Novel synthetic 9-benzyloxyacridine analogue as both tyrosine kinase and topoisomerase I inhibitor[J]. Chin. Chem. Lett.,
2013,24:677-680.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2013.05.018
-
[16]
Cui Z., Li X., Li L.. Design, synthesis and evaluation of acridine derivatives as multi-target Src and MEK kinase inhibitors for anti-tumor treatment[J]. Bioorg. Med. Chem.,
2016,24:261-269.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.12.011
-
[17]
Li L., Zhang C.L., Song H.R.. Discovery of novel dual inhibitors of VEGFR and PI3 K kinases containing 2-ureidothiazole scaffold[J]. Chin. Chem. Lett.,
2016,27:1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2015.09.008
-
[18]
Zhang W., Zhang B., Zhang W.. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of 9-benzylamino-6-chloro-2-methoxy-acridine derivatives as potent DNAbinding ligands and topoisomerase Ⅱ inhibitors[J]. Eur. J. Med. Chem.,
2016,116:59-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.03.066
-
[19]
Liao J.J.L.. Molecular recognition of protein kinase binding pockets fordesign of potent and selective kinase inhibitors[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2007,50:409-424.
doi: 10.1021/jm0608107
-
[20]
Cai M., Hu J., Tian J.L.. Novel hybrids fromN-hydroxyarylamideand indole ring through click chemistry as histone deacetylase inhibitors with potent antitumor activities[J]. Chin. Chem. Lett.,
2015,26:675-680.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2015.03.015
-
[21]
Bhattacharya S.K., Cox E.D., Kath J.C.. Achieving selectivity between highly homologous tyrosine kinases:a novel selective erbB2 inhibitor[J]. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,
2003,307:267-273.
doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01160-4
-
[22]
Bali P., Pranpat M., Swaby R.. Activity of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid against human breastcancercells with amplification ofHer-2[J]. Clin. Cancer Res.,
2005,11:6382-6389.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0344
-
[23]
Scroggins B.T., Robzyk K., Wang D.. An acetylation site in the middle domain of Hsp90 regulates chaperone function[J]. Mol. Cell,
2007,25:151-159.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.12.008
-
[24]
Steiner P., Joynes C., Bassi R.. Tumor growth inhibition with cetuximab and chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer xenografts expressing wildtype and mutated epidermal growth factor receptor[J]. Clin. Cancer Res.,
2007,13:1540-1551.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1887
-
[25]
Chang S., Zhang L., Xu S.. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel conformationally constrained inhibitors targeting epidermal growth factor receptor threonine790!methionine790 mutant,[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2012,55:2711-2723.
doi: 10.1021/jm201591k
-
[26]
Chu B., Liu F., Li L.. A benzimidazole derivative exhibiting antitumor activity blocks EGFR and HER2 activity and upregulates DR5 in breast cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis.,
2015,6e1686.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.25
-
[27]
Xing Z., Tang X., Gao Y.. The human LIS1 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and plays a tumor suppressor function[J]. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,
2011,409:193-199.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.117
-
[28]
Merlino G., Xu Y., Ishii S.. Amplification and enhanced expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in A431 human carcinoma cells[J]. Science,
1984,224:417-419.
doi: 10.1126/science.6200934
-
[29]
Konecny G.E., Pegram M.D., Venkatesan N.. Activity of the dual kinase inhibitor lapatinib (GW572016) against HER-2-overexpressing and trastuzumab-treated breast cancer cells[J]. Cancer Res.,
2006,66:1630-1639.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1182
-
[30]
Wood E.R., Truesdale A.T., McDonald O.B.. A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016(Lapatinib):relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells[J]. Cancer Res.,
2004,64:6652-6659.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1168
-
[31]
Lauffer B.E.L., Mintzer R., Fong R.. Histone deacetylase (hdac) inhibitor kinetic rate constants correlate with cellular histone acetylation but not transcription and cell viability[J]. J. Biol. Chem.,
2013,288:26926-26943.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.490706
-
[32]
Patel G., Karver C.E., Behera R.. Kinase scaffold repurposing for neglected disease drug discovery:discovery of an efficacious lapatanib-derived lead compound for trypanosomiasis[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2013,56:3820-3832.
doi: 10.1021/jm400349k
-
[33]
Gu G., Wang H., Liu P.. Discovery and structural insight of a highly selective protein kinase inhibitor hit through click chemistry[J]. Chem. Commun.,
2012,48:2788-2790.
doi: 10.1039/c1cc15851a
-
[34]
Chen J.B., Chern T.R., Wei T.T.. Design and synthesis of dual-action inhibitors targeting histone deacetylases and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase for cancer treatment[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2013,56:3645-3655.
doi: 10.1021/jm400179b
-
[35]
Hugenberg V., Riemann B., Hermann S.. Inverse 12, 3-Triazole-1-yl-ethyl substituted hydroxamates as highly potent matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors:(radio)synthesis, in vitro and first in vivo evaluation[J]. J. Med. Chem.,
2013,56:6858-6870.
doi: 10.1021/jm4006753

 Login In
Login In






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: