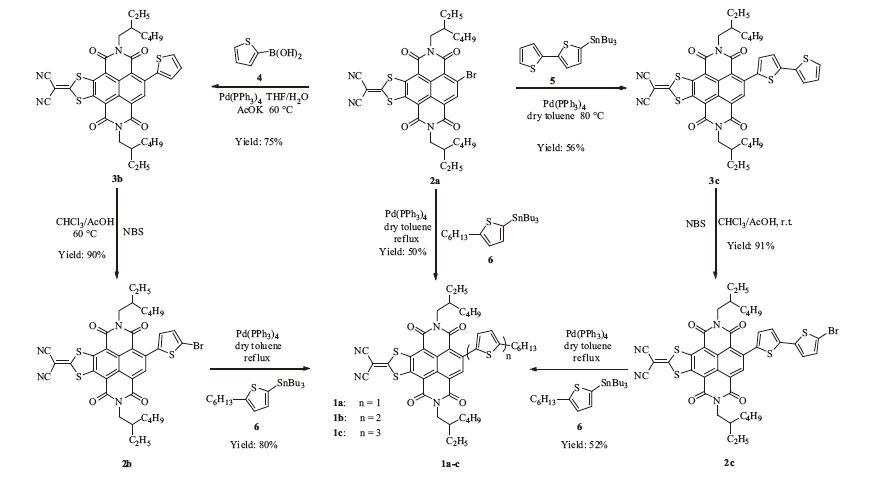
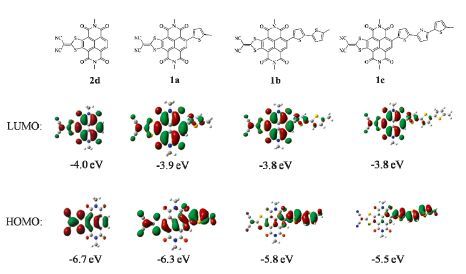
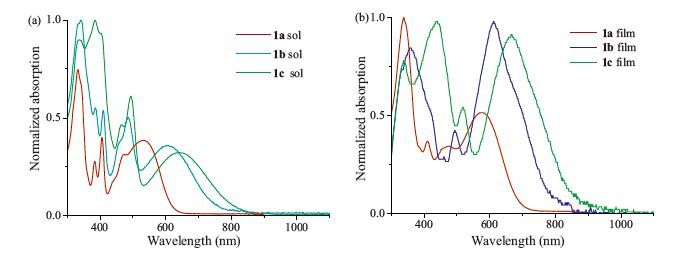
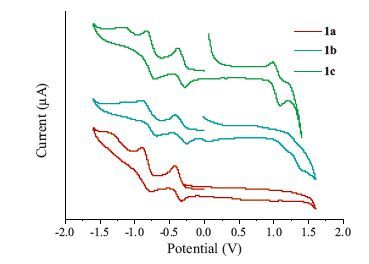
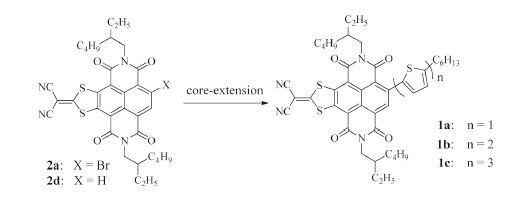
-
[1]
C. Wang, H. Dong, W. Hu. Semiconducting π-conjugated systems in fieldeffect transistors: a material odyssey of organic electronics[J]. Chem. Rev.,
2012,112:2208-2267.
doi: 10.1021/cr100380z
-
[2]
(a) C.L. Chochos, N. Tagmatarchis, V.G. Gregoriou. Rational design on n-type organic materials for high performance organic photovoltaics. RSC Adv., 2013, 3: 7160-7181;(b) X. Zhang, X. Li. Effect of the position of substitution on the electronic properties of nitrophenyl derivatives of fulleropyrrolidines: fundamental understanding toward raising LUMO energy of fullerene electron-acceptor. Chin. Chem. Lett., 2014, 25: 501-504;(c) T. Jiang, Z. Wang, B. Du, et al., Theoretical characterization of hole mobility in BTBPD. Chin. Chem. Lett., 2013, 24: 945-948.
-
[3]
R.H. Friend, R.W. Gymer, A.B. Holmes. Electroluminescence in conjugated polymers[J]. Nature,
1999,397:121-128.
doi: 10.1038/16393
-
[4]
G. Gelinck, P. Heremans, K. Nomoto. Organic transistors in optical displays and microelectronic applications[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2010,22:3778-3798.
doi: 10.1002/adma.200903559
-
[5]
H., A., T.J.Marks. n-Channel semiconductor materials design for organic complementary circuits[J]. Acc. Chem. Res.,
2011,44:501-510.
doi: 10.1021/ar200006r
-
[6]
(a) X. Gao, Z. Zhao. High mobility organic semiconductors for field-effect transistors. Sci. China Chem., 2015, 58: 947-968;(b) J. Dou, Y. Zheng, Z. Yao, et al., A cofacially stacked electron-deficient small molecule with a high electron mobility of over, 10 cm2 V-1 s-1 in air. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27: 8051-8055;(c) G. Xue, J. Wu, C. Fan, et al., Boosting the electron mobility of solution-grown organic single crystals via reducing the amount of polar solvent residues. Mater. Horiz., 2016, 3: 119-123.
-
[7]
L. Pandey, C. Risko, J.E. Norton. Donor-acceptor copolymers of relevance for organic photovoltaics: a theoretical investigation of the impact of chemical structure modifications on the electronic and optical properties[J]. Macromolecules,
2012,45:6405-6414.
doi: 10.1021/ma301164e
-
[8]
H. Usta, A. Facchetti, T.J. Marks. Air-stable, solution-processable n-channel and ambipolar semiconductors for thin-film transistors based on the indenofluorenebis( dicyanovinylene) core[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
2008,130:8580-8581.
doi: 10.1021/ja802266u
-
[9]
(a) P. Sonar, S.P. Singh, P. Leclere, et al., Synthesis, characterization and comparative study of thiophene-benzothiadiazole based donor-acceptor-donor (D-A-D) materials, J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19: 3228-3237;(b) Y. Cheng, S.H. Yang, C. Hsu. Synthesis of conjugated polymers for organic solar cell applications. Chem. Rev., 2009, 109: 5868-5923.
-
[10]
L. Bü rgi, M. Turbiez, R. Pfeiffer. High-mobility ambipolar near-infrared light-Emitting polymer field-effect transistors[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2008,20:2217-2224.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095
-
[11]
A. Facchetti, M.H. Yoon, C.L. Stern. Building blocks for n-type organic electronics: regiochemically modulated inversion of majority carrier sign in perfluoroarene-modified polythiophene semiconductors[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,
2003,42:3900-3903.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773
-
[12]
B. Sun, W. Hong, Z.Q. Yan. Record high electron mobility of, 6.3 cm2 V-1 s-1 achieved for polymer semiconductors using a new building block[J]. Adv. Mater.,
2014,26:2636-2642.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.17
-
[13]
H. Krü ger, S. Janietz, D. Sainova. Hybrid supramolecular naphthalene diimide-thiophene structures and their application in polymer electronics[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater.,
2007,17:3715-3723.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1616-3028
-
[14]
(a) X. Gao, C. Di, Y. Hu, et al., Core-expanded naphthalene diimides fused with, 2-(1, 3-dithiol-2-ylidene) malonitrile groups for high-performance, ambient-stable, solution-processed n-channel organic thin film transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132: 3697-3699;(b) Y. Hu, Y. Qin, X. Gao, et al., One-pot synthesis of core-expanded naphthalene diimides: enabling n-substituent modulation for diverse n-type organic materials. Org. Lett., 2012, 14: 292-295;(c) X. Gao, Y. Hu. Development of n-type organic semiconductors for thin film transistors: a viewpoint of molecular design. J. Mater. Chem. C., 2014, 2: 3099-3117.
-
[15]
S.L. Suraru, U. Zschieschang, H. Klauk. A core-extended naphthalene diimide as a p-channel semiconductor[J]. Chem. Commun.,
2011,47:11504-11506.
doi: 10.1039/c1cc15144d
-
[16]
(a) M.L. Tang, T. Okamoto, Z. Bao. High-performance organic semiconductors: asymmetric linear acenes containing sulphur. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128: 16002-16003;(b) M.L. Tang, M.E. Roberts, J.J. Locklin, et al., Structure property relationships: asymmetric oligofluorene-thiophene molecules for organic TFTs. Chem. Mater., 2006, 18: 6250-6257.
-
[17]
B. Leng, D. Lu, X. Jia. Synthesis of monolateral and bilateral sulfur-heterocycle fused naphthalene diimides (NDIs) from monobromo and dibromo NDIs[J]. Org. Chem. Front.,
2015,2:372-377.
doi: 10.1039/C4QO00252K
-
[18]
A. Mishra, R.K. Behera, P.K. Behera. Cyanines during the, 1990s: a review[J]. Chem. Rev.,
2000,100:1973-2012.
doi: 10.1021/cr990402t

 Login In
Login In






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: